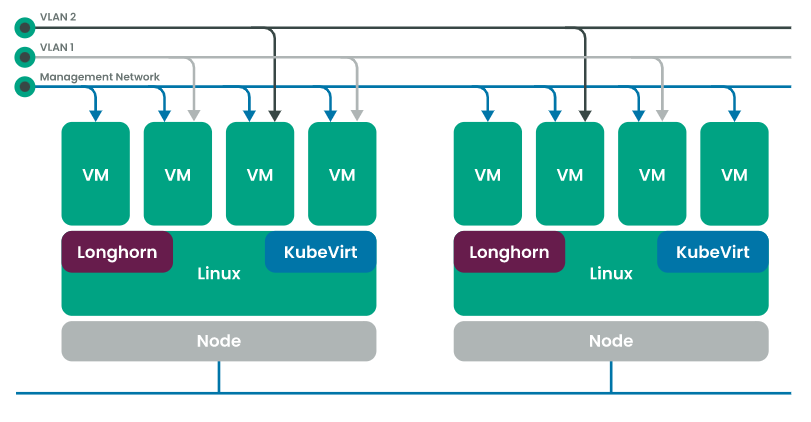
Rancher Harvester is an open-source hyper-converged infrastructure platform designed to run modern cloud-native workloads on bare metal servers and it is completely open-source and free to use. Traditional Type 1 Hypervisors are complicated to set up on bare-metal hardware...













